Contents
- 1 Introduction:
- 2 Background of Ayodhya Dispute:
- 3 Story behindAyodhya:
- 4 Reasons Behind Ayodhya Temple:
- 5 The Mosque in Ayodhya:
- 6 Legal Battles and Resolutions:
- 7 Impact on Society:
- 8 Historical Significance and Heritage Preservation:
- 9 International Attention and Perception:
- 10 Public Perception and Reconciliation Efforts:
- 11 Tourism and Economic Implications:
- 12 Continued Legal Implications:
- 13 Global Perspectives on Religious Tolerance:
- 14 Conclusion:
Introduction:
The Ayodhya dispute stands as a poignant chapter in India’s history, weaving together intricate legal narratives and deep-rooted religious sentiments. This article delves into the complex legal history of Ayodhya, unraveling the background, the story behind Ayodhya, the reasons for the Ayodhya temple , and the mosque that once graced this sacred land.
Background of Ayodhya Dispute:
The Ayodhya dispute is centered on a piece of land in the city of Ayodhya in Uttar Pradesh, India. The controversy is primarily a clash between the Hindu and Muslim communities over a site traditionally believed to be the birthplace of Lord Rama, a significant figure in Hinduism.
Story behindAyodhya:
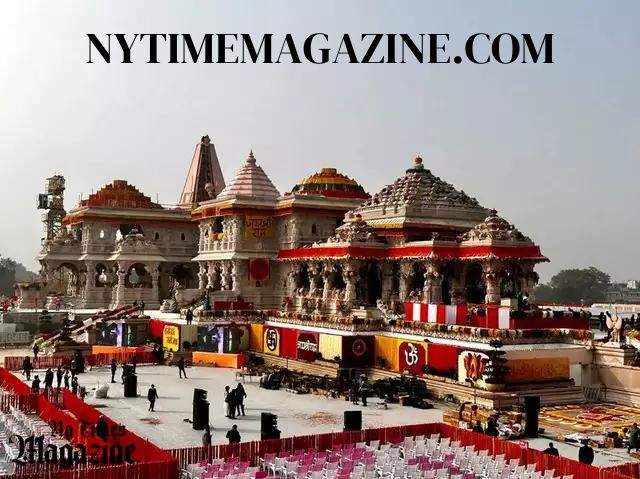
Ayodhya, often referred to as the birthplace of Lord Rama, holds immense religious significance for Hindus. The ancient city is woven into the fabric of Indian mythology, celebrated for its association with the Ramayana, an epic that narrates the life and adventures of Lord Rama. The belief in Rama’s birth in Ayodhya has been a cornerstone of Hindu faith for centuries, contributing to the emotional intensity surrounding the Ayodhya dispute.
Reasons Behind Ayodhya Temple:
The roots of the Ayodhya temple lie in the Hindu belief that the revered deity, Lord Rama, was born at the disputed site. Devotees have long envisioned a grand temple dedicated to Lord Rama at this sacred spot. The demand for the construction of the temple gained momentum in the late 20th century, leading to a legal and social tug-of-war between the Hindu and Muslim communities.
The Mosque in Ayodhya:
The Bari Masjid, a mosque built by Mughal Emperor Babur in the 16th century, once stood at the disputed site in Ayodhya. The mosque’s existence became a focal point of contention as the Hindu community claimed that it was constructed on the ruins of a pre-existing Hindu temple marking Lord Rama’s birthplace.
Legal Battles and Resolutions:
The legal history of the Ayodhya dispute is a labyrinth of court cases, appeals, and verdicts. One of the landmark moments was the demolition of the Bari Masjid in 1992 by Hindu activists, leading to widespread communal tensions. The legal battle reached its zenith with the Supreme Court of India’s verdict in 2019, which awarded the disputed site to the Hindus for the construction of a temple, while allocating an alternate piece of land to the Muslims for the construction of a mosque.
Impact on Society:
The Ayodhya dispute transcends legal dimensions; it has had a profound impact on India’s social fabric. Communal tensions, protests, and debates surrounding the issue have shaped the nation’s discourse on religious harmony and cultural diversity. The resolution, as provided by the Supreme Court, aimed to strike a balance between the two communities and pave the way for peaceful coexistence.
Historical Significance and Heritage Preservation:
The Ayodhya dispute also sheds light on the broader issue of heritage preservation. The city’s historical significance extends beyond its religious connotations, encompassing a rich tapestry of cultural and architectural heritage. As the Ayodhya temple takes shape, there is a growing emphasis on preserving the city’s diverse historical layers, ensuring that its cultural richness is not overshadowed by the dispute but rather celebrated as an integral part of India’s heritage.
International Attention and Perception:
The Ayodhya dispute has not escaped the attention of the international community. The global perception of India, particularly concerning its religious and cultural harmony, has been influenced by the events surrounding Ayodhya. As the nation grapples with this complex issue, it simultaneously navigates the challenge of presenting itself as a pluralistic society that value and protects its diverse cultural and religious identities.
Public Perception and Reconciliation Efforts:
The public’s perception of the Ayodhya dispute is a dynamic aspect influenced by various factors such as media coverage, political narratives, and community initiatives. While the legal resolution provides a formal conclusion, ongoing efforts are essential to promote reconciliation at the grassroots level. Initiatives that encourage interfaith dialogues, cultural exchange, and mutual understanding can contribute to healing the communal scars left by the prolonged dispute.
Tourism and Economic Implications:
As Ayodhya transforms with the construction of the temple, there are potential economic implications, particularly in the realm of tourism. The city, already a significant pilgrimage site, may witness an influx of tourists eager to witness the construction of the Ayodhya temple. This surge in tourism can bring economic opportunities to the region, but it also requires careful planning to ensure sustainable development and the preservation of Ayodhya’s cultural and historical integrity.
Continued Legal Implications:
Despite the Supreme Court’s verdict, legal implications may persist as stakeholders navigate issues related to land allocation, property rights, and potential legal challenges. Monitoring the legal landscape surrounding Ayodhya remains essential as it evolves, influencing the broader conversation on property rights, religious freedom, and the role of the judiciary in addressing complex and sensitive disputes.
Global Perspectives on Religious Tolerance:
The Ayodhya dispute reverberates globally, prompting discussions on religious tolerance, freedom of worship, and the role of secular institutions in mediating religious conflicts. Nations worldwide observe how India addresses this intricate issue, offering lessons and insights for fostering religious harmony and pluralism in diverse societies. Ayodhya, in this context, becomes a microcosm reflecting the broader challenges and opportunities in maintaining peace amidst religious diversity.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Ayodhya dispute encapsulates the myriad complexities woven into India’s social, cultural, and legal fabric. As the nation embarks on a new chapter marked by the construction of the Ayodhya temple, there is an opportunity for introspection, healing, and fostering a sense of unity in diversity. Navigating the aftermath of such a prolonged and sensitive dispute requires a collective effort from all sections of society, emphasizing the shared values that bind communities together.
The Ayodhya dispute is not merely a historical footnote but a living narrative that continues to shape India’s identity. In the spirit of progress and coexistence, the nation can draw upon the lessons learned from this complex journey, fostering a future where religious diversity is celebrated, and the rich tapestry of India’s cultural heritage is preserved for generations to come.